Voting Process

1. Vote Preparation (Organizer)
- Reward Funding: Before a vote begins, the organizer deposits the total amount of reward tokens (e.g., Punk Tokens) directly into the VoteNFT smart contract. This contract will act as a secure vault, or treasury, for the rewards.
- Vote Creation & Deployment: The organizer uses a tool like the Punkpoll builder to define the vote's rules: the content (linked via
ipfsHash), voting period, voter eligibility, and reward amount. These rules are set as immutable variables when the VoteNFT contract is deployed on the Avalanche blockchain. Once deployed, these rules cannot be altered by anyone. - Issuing Voting Rights: The organizer mints and distributes unique ERC-721 voting-right NFTs to the wallets of all verified and eligible voters. This NFT serves as a verifiable on-chain credential to participate in that specific vote.
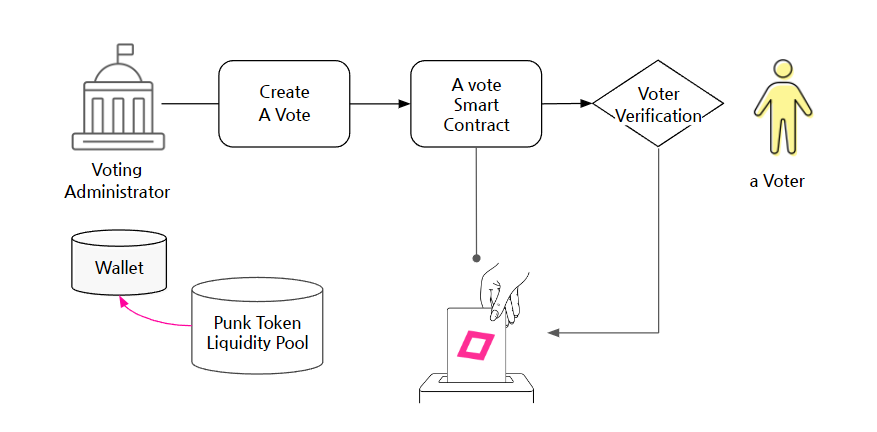
2. The Voting Process: A Three-Stage Lifecycle
Punkpoll’s process is designed for simplicity and security, separating user actions from complex on-chain transactions.
- Stage 1: Off-Chain Participation (Voter) A voter uses the Punkpoll interface (web/app) to cast their vote. The response data is stored off-chain (e.g., on IPFS), which generates a unique data fingerprint called an
ipfsHash. The voter then simply provides a cryptographic signature to approve the submission of thisipfsHash, without needing to handle gas fees directly. - Stage 2: On-Chain Submission (Trusted Forwarder) The signed request is sent to a Trusted Forwarder (a relayer service). This forwarder pays the gas fee (AVAX) and submits the transaction to the VoteNFT contract on the voter's behalf. This mechanism, known as gas abstraction, allows for a Web2-like user experience.
- Stage 3: Atomic Execution (VoteNFT Smart Contract) Upon receiving the transaction from the forwarder, the VoteNFT contract executes all of the following steps atomically (as one indivisible operation):
- Verification: It verifies the voter's eligibility, checks for duplicate participation, and confirms the caller is an authorized forwarder.
- NFT Retrieval: It automatically transfers the voter's specific voting-right NFT back to the contract, marking the vote as officially cast.
- Reward Distribution: It immediately sends the predetermined reward token from its internal treasury to the voter's wallet.
- On-Chain Record: It emits a
Participatedevent, permanently logging the voter's address, the returned NFT's ID, and theipfsHashof their vote data on the blockchain.
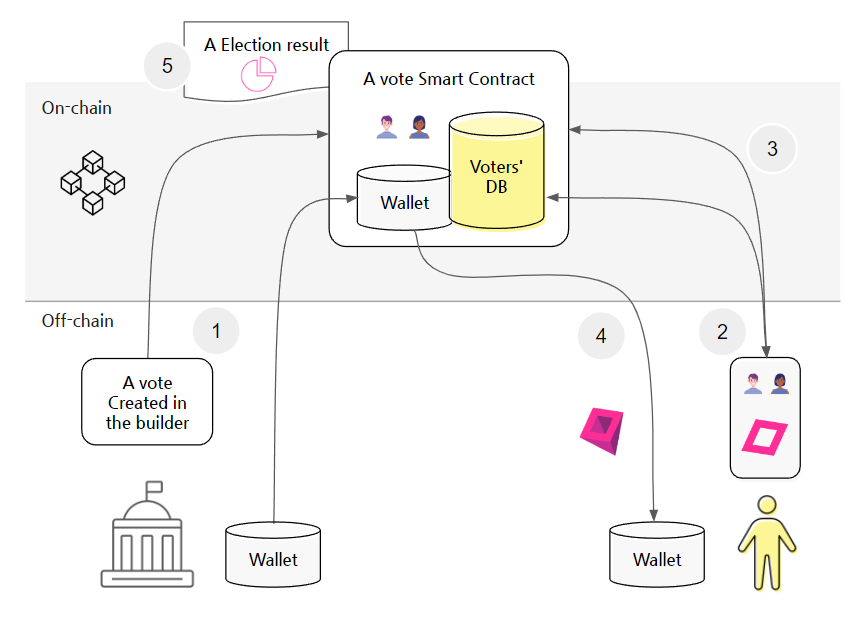
3. Verifying Participation
After voting, a voter can confirm their participation was successful and recorded correctly. There is no separate "receipt NFT." Instead, verification is achieved by:
- Receiving the Reward: The arrival of the reward token in their wallet serves as an immediate, practical receipt.
- Checking the Blockchain: The voter can use a blockchain explorer to find the transaction. The emitted event log will show their wallet address and the unique
ipfsHashcorresponding to their vote, proving their data was included in the official tally without revealing the vote's content.
4. On-Chain vs. Off-Chain Roles
- Off-Chain: This includes all user-facing activities. Creating the vote content, storing detailed response data on IPFS, generating the
ipfsHash, and the user’s cryptographic signature. - On-Chain (Avalanche): This is the domain of the monolithic VoteNFT smart contract. It handles all critical logic: rule enforcement, secure storage of rewards, and the atomic execution of NFT retrieval, reward distribution, and data logging. This integrated architecture ensures trust-minimized, tamper-proof, and cost-efficient operations.